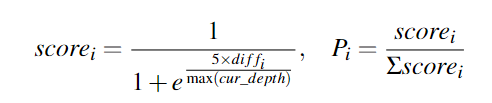论文:FUGIO: Automatic Exploit Generation for PHP Object Injection Vulnerabilities
源码:https://github.com/WSP-LAB/FUGIO
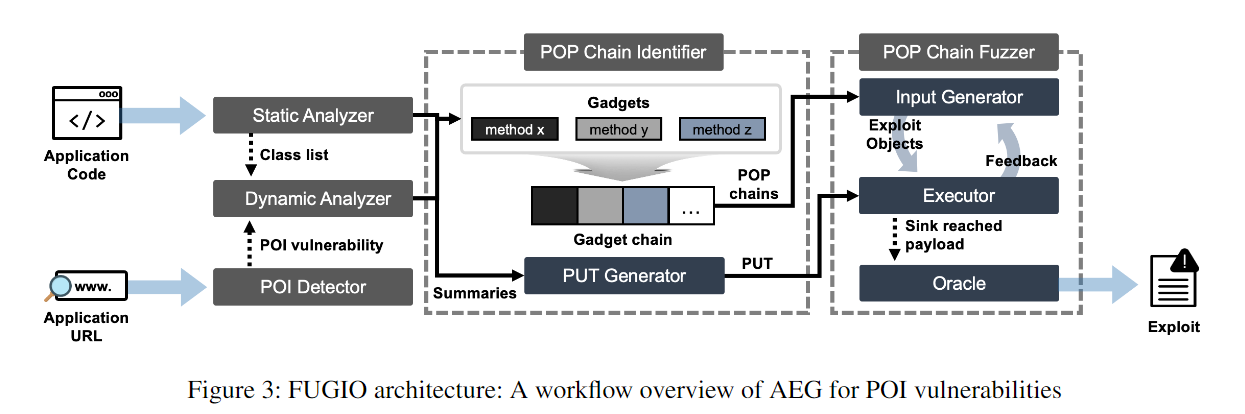
整体架构如图所示,先通过POP Chain Identifier静态分析出潜在的PHP反序列化漏洞利用链,再通过POP Chain Fuzzer进行动态的验证以及POC的生成。
这里主要关注POP Chain Fuzzer部分,算法伪代码描述如下:
主要逻辑位于Fuzzer/FuzzSlave.php中的RunFuzz方法
Seed
Seed对应的类为SeedNode,其中比较重要的属性包括:
$input_tree,对应一条将要生成的反序列化利用链,里面会记录类名以及该类各个属性的值,也就是论文中说的property tree
$goal_depth,在POP链(来自POP Chain Identifier的结果)中已执行的最大深度
depth,好像没到达sink点的话就是$goal_depth-1,到达了sink点就一样
$select_count,seed被选择过的次数
对应于伪代码的1-3行,FUGIO首先生成一个seed并加入seed_pool
1 2 3 4 if ($this ->seed_pool->root == NULL ) { $this ->seed_pool->SetRoot($this ->GenerateFirstSeed()); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 function GenerateFirstSeed () $payload_creator = new PayloadCreator(); $new_seed = new SeedNode(); $new_seed->class_template = $payload_creator->MakeGadgetTemplate($this ->gadget[0 ]); $new_seed->input_tree = $payload_creator->GenerateRandomProperties( $new_seed->class_template, $this ->gadget[0 ], $this ->file_chain ); $new_seed->parent = NULL ; $new_seed->goal_depth = 0 ; $new_seed->depth = -1 ; $new_seed->select_count = 0 ; $new_seed->seed_idx = 0 ; $this ->seed_pool->seed_idx += 1 ; return $new_seed; }
举个例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <?php class Foo public $p; public function __destruct () $this ->o->jump($this ->a); } } class Bar public function jump ($a) $this ->o2->evil($a); } } class Baz public function evil ($a) if ($this ->con == 5 ) { system($a); } } } unserialize(base64_decode($_GET['input' ]));
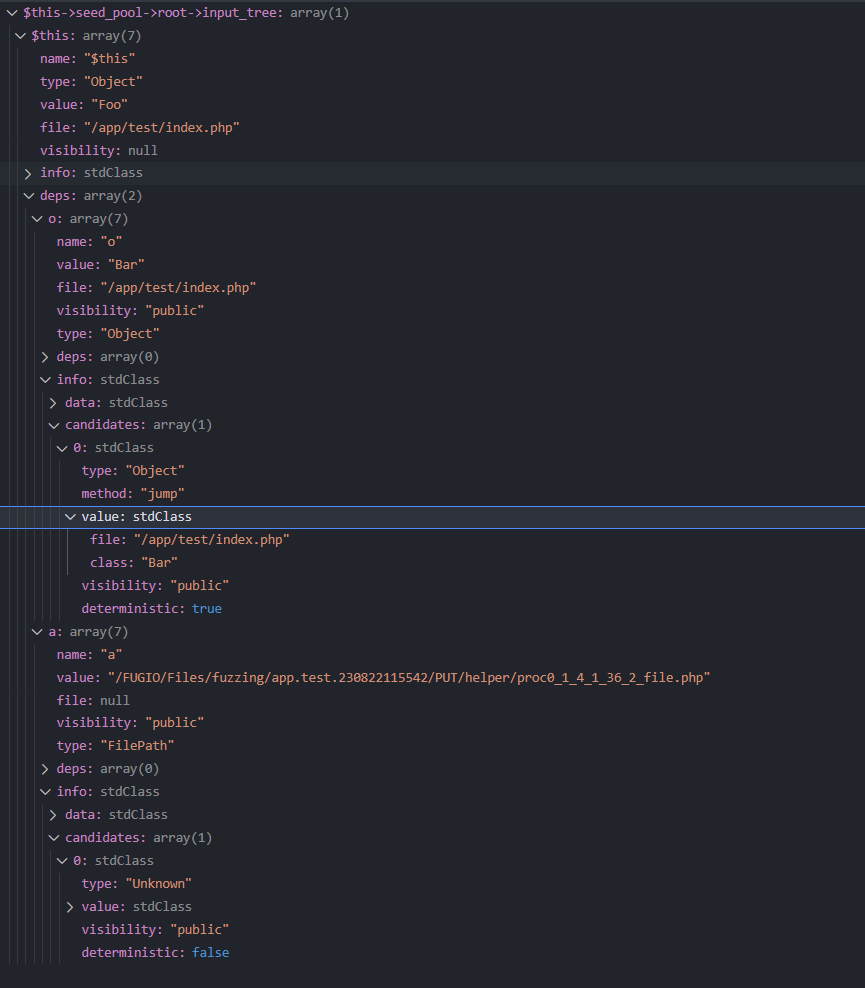
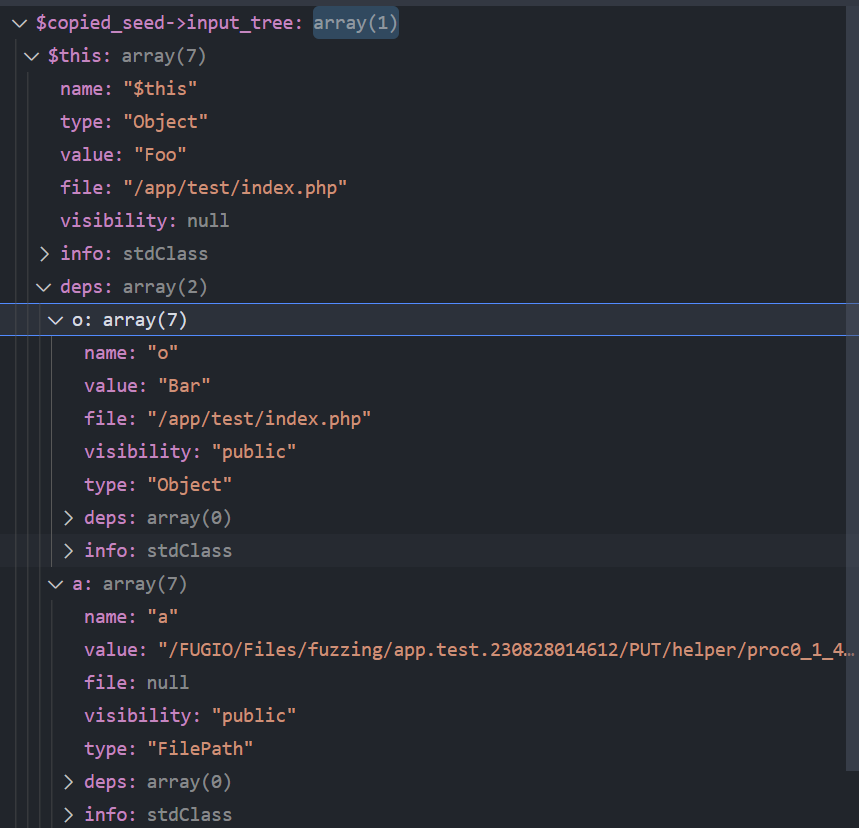
此时生成的第一个seed的input_tree为:
可以看到此时的seed只包含链子中第一个gadget的结构,因为Foo::__destruct中会调用$this->o属性的jump方法,$this->o被设为了存在jump方法的Bar类对象,而$this->a则被随机设为了FilePath类型
Select Seed
seed选择的实现位于Fuzzer/SeedTree.php中的CherryPick方法,对应伪代码第5行,分为3个步骤
将seed按深度、被选择的次数以及是否到达sink点3个指标进行分类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 $seed_dict = array (); $seed_queue = array ($this ->root); while ($seed = array_shift($seed_queue)) { if (!array_key_exists($seed->goal_depth, $seed_dict)) { $goal_depth = $seed->goal_depth + 1 ; if ($max_goal_depth <= $goal_depth) { $max_goal_depth = $goal_depth; } $seed_dict[$goal_depth]['TRY_O' ] = array (); $seed_dict[$goal_depth]['TRY_X' ] = array (); $seed_dict[$goal_depth]['TRY_O_SINK_REACHED' ] = array (); $seed_dict[$goal_depth]['TRY_X_SINK_REACHED' ] = array (); } if ($seed->select_count == 0 ) { array_push($seed_dict[$goal_depth]['TRY_X' ], $seed); if ($seed->sink_reached['reach' ] == True ) { array_push($seed_dict[$goal_depth]['TRY_X_SINK_REACHED' ], $seed); } } else { array_push($seed_dict[$goal_depth]['TRY_O' ], $seed); if ($seed->sink_reached['reach' ] == True ) { array_push($seed_dict[$goal_depth]['TRY_O_SINK_REACHED' ], $seed); } } foreach ($seed->child as $child_seed) { array_push($seed_queue, $child_seed); } }
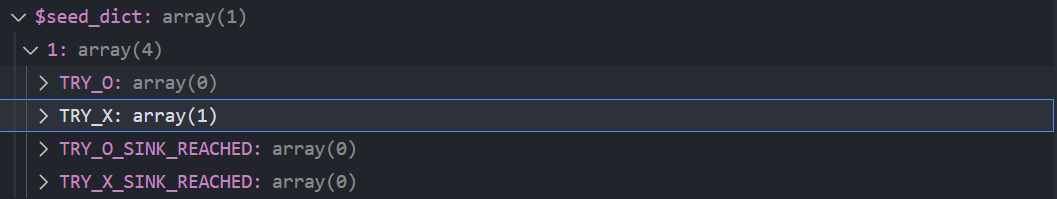
最终$seed_dict的结构如下:
其中索引1代表这些seeds的$goal_depth都为0,TRY_X代表未被选择过的seed,TRY_O则相反。如果1个seed到达了sink点,则它会同时出现在TRY_X和TRY_X_SINK_REACHED或者TRY_O和TRY_O_SINK_REACHED中
按照公式计算不同深度seed的分数,根据分数按不同概率选择某一个深度的seeds
计算分数的公式:
其中diff为当前seed的goal_depth和整个链子深度的差值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 $depth_scores = array (); $depth_sum = 0 ; foreach ($seed_dict as $goal_depth => $seeds) { $power = (5 * ($fianl_goal_depth - $goal_depth) / ($max_goal_depth)); $depth_score = 1 /(1 +pow(exp(1 ), $power)); array_push($depth_scores, $depth_score); $depth_sum += $depth_score; } $depth_probability = array (); foreach ($depth_scores as $goal_depth => $depth_score) { array_push($depth_probability, $depth_score/$depth_sum); } $selected_depth_array = $this ->RandomChoiceByProbability($seed_dict, $depth_probability);
最终的$selected_depth_array就是被选择的某个深度的所有seeds
最终选择seed
存在到达sink点的seed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 if ($count_sink_reached > 0 ) { $try_o_prob_sum = 0 ; $sink_reached_try_o_prob_sum = 0 ; foreach ($selected_depth_array['TRY_O' ] as $try_o_seed) { $power = $try_o_seed->select_count / ($const_exp * $const_max_try); $try_o_alpha = 2 / (1 + pow($const_exp, $power)); if ($try_o_seed->sink_reached['reach' ]) { $try_o_prob = (($const_sink_weight) / ($count_try_o_sink_reached + $count_try_x_sink_reached)) * $try_o_alpha; $sink_reached_try_o_prob_sum += $try_o_prob; } else { $try_o_prob = ((1 - $const_sink_weight) / (($count_try_o + $count_try_x) - ($count_try_o_sink_reached + $count_try_x_sink_reached))) * $try_o_alpha; $try_o_prob_sum += $try_o_prob; } array_push($seeds, $try_o_seed); array_push($seed_probabilities, $try_o_prob); } foreach ($selected_depth_array['TRY_X' ] as $try_x_seed) { if ($try_x_seed->sink_reached['reach' ]) { $try_x_prob = ($const_sink_weight - $sink_reached_try_o_prob_sum) / ($count_try_x_sink_reached); } else { $try_x_prob = (((1 - $const_sink_weight) - ($try_o_prob_sum)) / (($count_try_o + $count_try_x) - ($count_try_o_sink_reached + $count_try_x_sink_reached) - ($count_try_o))); } array_push($seeds, $try_x_seed); array_push($seed_probabilities, $try_x_prob); } }
其中的$const_sink_weight为0.9,也就是论文中说的:
When the seed pool includes seeds that reach the sink,
不存在到达sink点的seed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 else { $try_o_prob_sum = 0 ; foreach ($selected_depth_array['TRY_O' ] as $try_o_seed) { $power = $try_o_seed->select_count / ($const_exp * $const_max_try); $try_o_alpha = 2 / (1 + pow($const_exp, $power)); $try_o_prob = (1 / ($count_try_o + $count_try_x)) * $try_o_alpha; array_push($seeds, $try_o_seed); array_push($seed_probabilities, $try_o_prob); $try_o_prob_sum += $try_o_prob; } foreach ($selected_depth_array['TRY_X' ] as $try_x_seed) { $try_x_prob = (1 - $try_o_prob_sum) / ($count_try_x); array_push($seeds, $try_x_seed); array_push($seed_probabilities, $try_x_prob); } }
也是类似,TRY_O和TRY_X的计算方式不同,更倾向于选择TRY_X
Mutation
伪代码第6行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 $copied_seed->input_tree = $payload_creator->MakeAuxiliaryTemplateWithProp( $copied_seed->input_tree, $this ->gadget[$selected_seed->depth + 1 ], $this ->cand_props_hash_table ); $copied_seed->input_tree = $payload_creator->SetMutateProperties( $copied_seed->input_tree, $this ->file_chain, $this ->gadget, $this ->cand_class, $this ->cand_foreach, $this ->hinting_infos, $copied_seed->array_hinting, $copied_seed->array_object );
Add New Properties
实现位于/Fuzzer/PayloadCreator.php中的MakeAuxiliaryTemplateWithProp方法
这里会随机添加一些类中明确定义但在给定方法中没有直接使用的属性,比如上面那个例子中虽然Foo::__destruct中没有用到$p,但仍然有一定概率将$p添加到input_tree中,虽然并不知道这样有啥用…
1 2 3 4 $gen_aux_probability = rand(1 , 100 ); if ($gen_aux_probability > MAKE_AUX_PROP) { return $input_tree; }
遍历该类明确定义的属性($gadget_info->prop_list),按照一定概率保存到$aux_props
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 $prop_list = $gadget_info->prop_list; $aux_props = array (); foreach ($prop_list as $prop) { $gen_aux_sub_probability = rand(1 , 100 ); if ($gen_aux_sub_probability <= MAKE_AUX_SUB_PROP) { array_push($aux_props, $prop); } }
添加到seed中去,new_aux_props中保存的是$aux_props中属性构造的属性树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 if ($node['value' ] == $gadget_info->class and $node['file' ] == $gadget_info->file) { foreach ($new_aux_props as $new_obj_property) { $new_add_flag = True ; foreach ($node['deps' ] as $obj_property_key => $obj_property_value) { if ($new_obj_property['name' ] == $obj_property_value['name' ]) { $new_add_flag = False ; break ; } } if ($new_add_flag) { $adding_props[$new_obj_property['name' ]] = $new_obj_property; } } $node['deps' ] = $node['deps' ] + $adding_props; }
除了prop_list之外还会添加prop_candidates中的属性,没看懂啥时候会用到这个,试了几个benchmark感觉像是废的…
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 $aux_props_cands = array (); foreach ($cand_props_hash_table as $cand_class => $props_in_class) { foreach ($props_in_class as $prop_in_class) { $gen_aux_sub_probability = rand(1 , 100 ); if ($gen_aux_sub_probability <= MAKE_AUX_SUB_PROP) { if (!array_key_exists($cand_class, $aux_props_cands)) { $aux_props_cands[$cand_class] = array (); } $aux_props_cands[$cand_class][$prop_in_class['name' ]] = $prop_in_class; } } }
Mutate Properties
对seed中的属性进行变异,实现位于/Fuzzer/PayloadCreator.php中的SetMutateProperties方法
针对Object类型进行变异时会随机从候选的类中随机选择。例如上面那个例子中__destruct中调用了$this->o的jump方法,候选的类就只有包含jump方法的Bar类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 elseif (rand(0 , 100 ) <= 70 ) { $obj_candidates = $candidates->candidates; if (!empty ($obj_candidates)) { $choice = rand(0 , count($obj_candidates) - 1 ); if (empty ($obj_candidates[$choice]->value)) { var_dump($prop['name' ]); echo $choice . "\n" ; var_dump($obj_candidates); exit (); } $parent_class = $obj_candidates[$choice]->value->class; $parent_file = $obj_candidates[$choice]->value->file; $prop['value' ] = $parent_class; $prop['visibility' ] = $obj_candidates[$choice]->visibility; $prop['file' ] = $parent_file; } else { $parent_class = $prop['value' ]; $parent_file = $prop['file' ]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 if ($mutate_probability > MUTATE_PROP and $prop['type' ] != "Unknown" ) { continue ; } switch ($value_type) { case 0 : $prop['type' ] = "String" ; $prop['value' ] = $this ->GetRandomString(); break ; case 1 : $prop['type' ] = "Int" ; $prop['value' ] = $this ->GetRandomInt(); break ; case 2 : $prop['type' ] = "Boolean" ; $prop['value' ] = $this ->GetRandomBoolean(); break ; case 3 : $prop['type' ] = "Array" ; if (count($array_hinting) != 0 ) { $prop['value' ] = $this ->GetHintingArray($file_chain, $array_hinting); } else { $prop['value' ] = $this ->GetRandomArray($file_chain); } break ; ......
此外对于ArrayObject类型的属性也有特殊的处理
PUT Generation
在POP Chain Identifier和POP Chain Fuzzer启动前,PUT Generator部分会在Files/fuzzing/目标目录.时间戳/PUT/生成以下文件:
class-带有命名空间的类名.php,所谓的PUT(Program Under Test),其实就是将每个类的定义拆分到单独的文件中,例如上面例子中会生成class-bar.php class-baz.php和class-foo.php
put-body.php,include_once所有的PUT
put-head.php,使用uopz对内置函数进行hook相关,似乎是废弃的没啥用
除此之外,FUGIO还会先调用Fuzzer/Instrumentor.php,使用phpParser对PUT进行插桩从而向Fuzzer提供feedback,这一步会在Files/fuzzing/app.xxx.xxxx/PUT/下生成以下文件:
inst-class-带有命名空间的类名.php,上述例子中生成的inst-class-baz.php为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 ...... <?php namespace { class Baz { public function evil ($a ) { $GLOBALS['Feedback_cls']->isBranchPassed('000000006b06bc4800000000724d4095', 'METHOD-ENTRY', debug_backtrace()); if ($GLOBALS['Feedback_cls' ]->isBranchPassed('000000006b06bc7100000000724d4095' , 'COND-PRE' , array ()) && $this ->con == 5 && $GLOBALS['Feedback_cls' ]->isBranchPassed('000000006b06bc7100000000724d4095' , 'COND-POST' , array ())) { $GLOBALS['Feedback_cls' ]->funcWrapped('system' , debug_backtrace(), '000000006b06bc7500000000724d4095' , 'Baz' , 'evil' , '1' , $a); } } } } namespace {} namespace { if (getenv ("FUZZ_CMD ") === "FuzzerInit ") { $GLOBALS['Feedback_cls']->initIfConstraint('000000006b06bc7100000000724d4095', array('TYPE_VALUE', 'con', 'Int', '5', 'IF')); } }
可以看到,原有的方法调用被包裹了一层$GLOBALS['Feedback_cls']->setMethodWrapped,条件分支则前后都被包裹了一个$GLOBALS['Feedback_cls']->isBranchPassed,并且方法的入口点也添加了一个$GLOBALS['Feedback_cls']->isBranchPassed
除此之外,在该文件的最后还添加了一个$GLOBALS['Feedback_cls']->initIfConstraint,该语句用于给Fuzzer提供属性具体值的hint,从而加快Fuzzer执行的速度
inst_PUT.php,其中包含了isBranchPassed以及setMethodWrapped等插桩方法的实现,以及对用户输入的反序列化进行测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 ...... class ConstraintFeedback {...... function isBranchPassed ($stmt_id, $type, $call_stack, $argv_array = array() ) { array_push($this ->BranchPath, array ("hash" => $stmt_id, "type" => $type, "call_stack" => $call_stack, "argvs" => $argv_array)); foreach ($this ->goalPath as &$goalPath) { if ($goalPath['hash' ] == $stmt_id) { $goalPath['hitCount' ] += 1 ; break ; } } return True ; } ...... $channel = $connection->channel(); $channel->queue_declare($rabbitmq_channel, false , false , false , true ); if (getenv("FUZZ_CMD" ) == "FuzzerInit" ) { $msg = new AMQPMessage(serialize($GLOBALS['Feedback_cls' ]->init_output)); } else { $msg = new AMQPMessage(serialize($feedback_output)); } $channel->basic_publish($msg, '' , $rabbitmq_channel); ...... $userInput = base64_decode($argv[1 ]); $fuzzed_class = unserialize($userInput); switch ($entry_magic_method) { case "__destruct" : unset ($fuzzed_class); break ; case "__construct" : break ; case "__call" : $fuzzed_class->non_existed_method(); break ; ......
Execution
伪代码第7行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 $executor = new Executor(); $copied_seed->fuzz_result = $executor->ExecutePutByPayloadTree( $this ->file_inst, $this ->file_chain, $copied_seed->input_tree, $this ->rabbitmq_settings, $this ->rabbitmq_connection, $this ->chain[0 ]->method, $this ->chain );
Executor::ExecutePutByPayloadTree首先调用Executor::MakePayloadPhpFile,该方法在Files/fuzzing/app.xxx.xxxx/PUT/PAYLOAD下生成当前seed对应的序列化文件,例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <?php ...... namespace {// case 3 $obj_Foo_0 = new Foo ; $obj_Foo_0->setProp('o' , new Bar); $obj_Foo_0->setProp('a' , 880065850 ); $obj_Foo_0->setProp('p' , "/FUGIO/Files/fuzzing/app.test.230828014612/PUT/helper/proc0_1_4_1_36_2_dir/" ); } namespace {echo base64_encode (serialize ($obj_Foo_0 ));} ?>
也就是按照seed中的属性树给对象属性挨个赋值,之后执行该文件即可获得该seed对应的序列化字符串
之后会调用之前Instrumentor阶段生成的Files/fuzzing/app.xxx.xxxx/PUT/inst_PUT.php,并将序列化字符串传递过去,从而执行该gadget
1 2 3 4 5 6 putenv("ENTRY_MAGIC_METHOD=" . $entry_magic_method); putenv("SEED_VALUE=" . $GLOBALS['SEED_VALUE' ]); shell_exec("php " . "-d max_execution_time=" . $GLOBALS['FUZZING_TIMEOUT' ] . " " . "-d memory_limit=" . MEMORY_LIMIT . " " . $file_inst . " " . $this ->serialized_string);
Feedback
总共有4类Feedback:
There exist four types of feedback that the fuzzer leverages: 1) branch
Branch Coverage
伪代码第8 9行,判断是否到达了新的path以及对fuzz结果的分析(两者顺序和伪代码中反过来)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 if ($this ->seed_pool->IsNewPath($copied_seed)) { $analyzed_result = $executor->AnalyzeExecutedResult( $copied_seed->fuzz_result['result' ], $this ->chain, $copied_seed ); ...... }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 function IsNewPath ($copied_seed) $seed_queue = array (); array_push($seed_queue, $this ->root); $seed_list = array (); while ($seed = array_shift($seed_queue)) { if ($seed->path_hash == $copied_seed->path_hash and $seed->goal_depth == $copied_seed->goal_depth and $seed->depth == $copied_seed->depth) { return False ; } foreach ($seed->child as $child_seed) { array_push($seed_queue, $child_seed); } } return True ; }
和其他seed挨个进行比对
将当前seed加入seed_pool,对应伪代码第10行
1 2 3 4 $copied_seed->depth = count($analyzed_result['gadget_pass_check' ]) - 1 ; $copied_seed->select_count = 1 ; $this ->seed_pool->AddSeed($selected_seed, $copied_seed, True );
The Depth of a Gadget Reached
伪代码17 18行,判断当前seed是否比变异前的seed到达了更深层的gadget,是的话根据当前seed再生成一个新seed加入seed_pool,其中包含了新到达的gadget
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 if ($copied_seed->depth > $selected_seed->depth) { if ($copied_seed->depth == 0 and $selected_seed->depth == -1 ) { $next_gadget_index = $copied_seed->depth + 1 ; } else { $next_gadget_index = $copied_seed->depth; } $next_gadget = $payload_creator->MakeGadgetTemplate( $this ->gadget[$next_gadget_index]); $merged_tree_list = $copied_seed->GetMergedTreeList($next_gadget); foreach ($merged_tree_list as $merged_tree) { $new_evolved_seed = new SeedNode(); $new_evolved_seed->template_tree = $merged_tree; $new_evolved_seed->input_tree = $payload_creator->SetMutateProperties( $new_evolved_seed->template_tree, $this ->file_chain, $this ->gadget, $this ->cand_class, $this ->cand_foreach, $this ->hinting_infos, $new_evolved_seed->array_hinting, $next_gadget ); $new_evolved_seed->goal_depth = $copied_seed->depth + 1 ; $new_evolved_seed->depth = $copied_seed->depth; $new_evolved_seed->select_count = 0 ; $new_evolved_seed->seed_idx = $this ->seed_pool->seed_idx; $new_evolved_seed->array_object = $next_gadget; $this ->seed_pool->seed_idx += 1 ; $this ->seed_pool->AddSeed($selected_seed, $new_evolved_seed, True ); } }
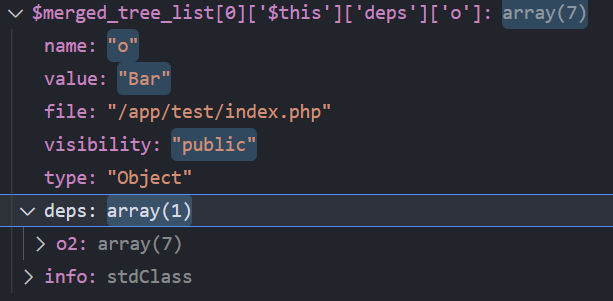
单说有点抽象,还是用上面那个例子。当Fuzzer第一次运行到该分支时,$copied_seed->input_tree类似于:
可以看到此时o被设置为了Bar类的对象,因此到达了第2层gadget,但其deps此时还是空的
而$merged_tree_list则会是补全了deps的$copied_tree:
Property Hinting
伪代码19-21行,这里有两类Hint:
条件分支的hint
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 $hinted_seeds = $this ->MakeHintedSeeds($copied_seed, $this ->hinting_data, $analyzed_result['passed_conds' ]); foreach ($hinted_seeds as $hinted_seed) { $hinted_seed->select_count = 0 ; $this ->seed_pool->seed_idx += 1 ; $hinted_seed->seed_idx = $this ->seed_pool->seed_idx; $this ->seed_pool->AddSeed($selected_seed, $hinted_seed, True ); }
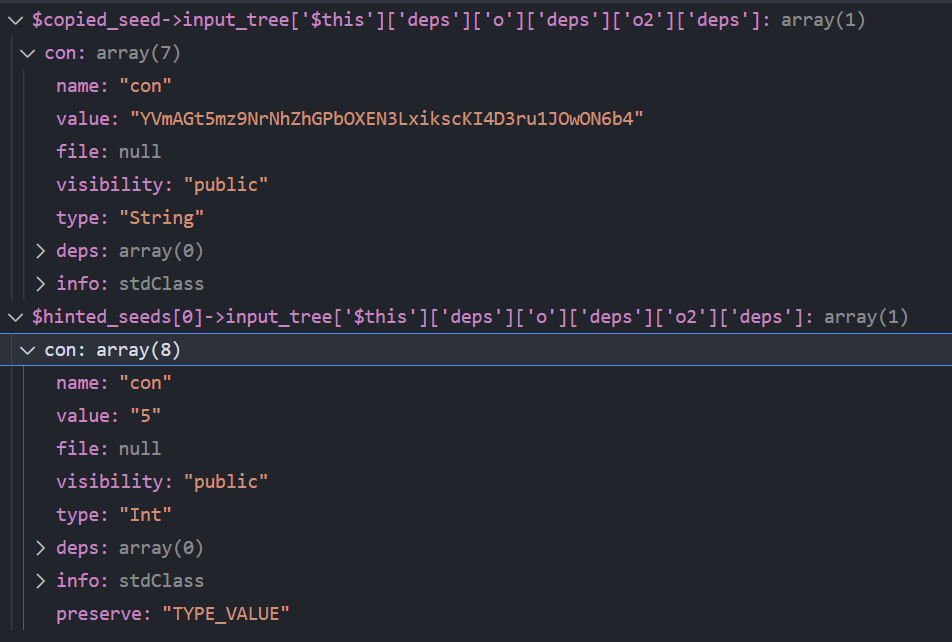
这里的hint来源于inst-class-xxx.php,其中包含了如果要进入某个分支某个属性需要的值,还是上面那个例子。当检测到$copied_seed能够到达该分支的COND-PRE并且已经具有该分支需要的属性时,就按照hint中的类型和值修改该属性
上面那个例子:
另外FUGIO只实现了==以及is_string这种的hint,<这种都不支持
数组索引的hint
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 $array_hinted_seed = $this ->MakeArrayHintedSeed( $copied_seed, $analyzed_result['array_fetch_list' ]); if ($array_hinted_seed != False ) { $array_hinted_seed->select_count = 0 ; $this ->seed_pool->seed_idx += 1 ; $array_hinted_seed->seed_idx = $this ->seed_pool->seed_idx; $this ->seed_pool->AddSeed($selected_seed, $array_hinted_seed, True ); }
处理的应该是这种情况:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class Baz public function evil ($a) if ($this ->con["key" ] == "value" ) { system($a); } } }
inst-class-baz.php中会多一个:
1 $this ->con[$GLOBALS['Feedback_cls' ]->ArrayFetch('000000001b7b9c78000000007cb15664' , '$this->con' , "key" , $this ->con, "key" , debug_backtrace())]
但这里的实现跟条件分支的hint有点不一样,并不会直接在$array_hinted_seed中把$this->con["key"]直接设成"value",只会给array_hinted_seed添加一个array_hinting属性。后续在变异(PayloadCreator::SetMutateProperties)的时候如果con的类型变异为Array或者ArrayObject的话有一定概率根据这个array_hinting属性设置一个"key"的索引(值还不会被设成"value"…)。感觉应该是没实现完或者写错了之类的,测试了几次根本不能成功fuzz出来
Reference Error
伪代码22-24行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 $revise_check = $this ->IsNeedRevise($copied_seed); if ($revise_check['result' ]) { if ($revise_check['type' ] == "NON_OBJECT_METHOD" ) { $added_prop_seeds = $this ->MakeAddPropSeeds($copied_seed); if ($added_prop_seeds != false ) { foreach ($added_prop_seeds as $added_prop_seed) { $new_added_seed = new SeedNode(); $new_added_seed->template_tree = $added_prop_seed; $new_added_seed->input_tree = $payload_creator->SetMutateProperties( $new_added_seed->template_tree, $this ->file_chain, $this ->gadget, $this ->cand_class, $this ->cand_foreach, $this ->hinting_infos, $new_added_seed->array_hinting, $copied_seed->array_object ); $new_added_seed->goal_depth = $copied_seed->depth + 1 ; $new_added_seed->depth = $copied_seed->depth; $new_added_seed->select_count = 0 ; $new_added_seed->seed_idx = $this ->seed_pool->seed_idx; $this ->seed_pool->seed_idx += 1 ; $this ->seed_pool->AddSeed($selected_seed, $new_added_seed, True ); } } } }
Furthermore, the fuzzer observes reference errors in the
虽然论文里说missing property or an incorrect object in the receiver,但代码中似乎只有后一种情况的处理,也不太知道啥情况能触发这个,正常情况下都会挑选有该方法的对象吧。
Exploit oracle
有空再写